Cited By (per year )
Cited By (per year )
RPG Interface Lab Projects
Published Projects
01. Extraction, Characterization, and Dual-Phase Dosage Optimization of Selective Tumor-suppressing Flavonoids for Inhibiting Cellular Proliferation in CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated HIF1α-Knockout Lung Adenocarcinoma: Integrated In Vitro and In Silico Analysis
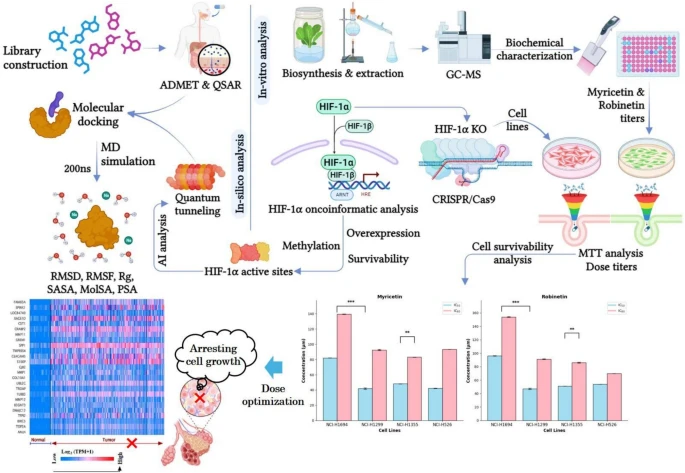
Abstract:HIF1α-driven lung adenocarcinoma, a fatal subtype of non-small cell lung cancer with 1.8 million deaths per year worldwide, highlights the need for new targeted treatments. The present work investigated the tumor-suppressing potential of the isolated and biochemically characterized flavonoids on HIF1α-driven lung adenocarcinoma through combined oncoinformatic profiling, molecular simulations, and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated HIF1α-knockout validation. Oncoinformatic profiling revealed HIF1α overexpression and promoter methylation as top predictors for poor prognosis. The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic screening identified myricetin and robinetin as lead flavonoids with potent HIF1α binding by molecular docking (-9.33 to -8.98 kcal/mol) and long-term stability in long-duration molecular dynamics simulations (200 ns), supported by structural dynamics (RMSD, RMSF, Rg, SASA, MolSA, and PSA) and binding free energy (MM/GBSA) parameters. A twenty five-gene cluster linked HIF1α to flavonoid metabolism, suggesting synergistic therapeutic targets. CRISPR-engineered HIF1α-deficient NCI-H1694 (gene effect score-negative) cells were less flavonoid-sensitive (IC50/IC80 34.5/68.2 μM) than HIF1α-proficient gene effect score-positive cell lines (NCI-H1299, NCI-H526, NCI-H1355; IC50 12.4–18.7 μM), validating HIF1α-dependent activity. These results place myricetin and robinetin in the category of precision drugs for HIF1α vulnerability, with potential applications for flavonoid-based therapies in lung adenocarcinoma. Through a combination of computational design, biosynthesis, and functional validation, this research presents a paradigm for next-generation, HIF1α-targeted oncology therapies.
02. Food loss and waste valorization offers a sustainable source of biopolymers in bioinks for 3D printing
Abstract:Food loss and waste (FLW) valorization remains challenging due to mixed properties and composition arising from seasonal and regional variations in food production. Here we examine the capacities of 3D printing for valorizing FLW streams, with a focus on FLW-based bioinks. We consider how waste management practices, 3D printing technology and emerging FLW valorization techniques could address challenges concerning raw material sourcing, improved material printability and suitable mechanical properties. Bioink ingredients incorporating biologically active compounds derived from FLW streams could offer tailored functionalities, supporting food preservation and economic, health and environmental sustainability benefits in line with the Sustainable Development Goals.
03. Machine learning-driven optimization of biphasic pretreatment conditions for enhanced lignocellulosic biomass fractionation
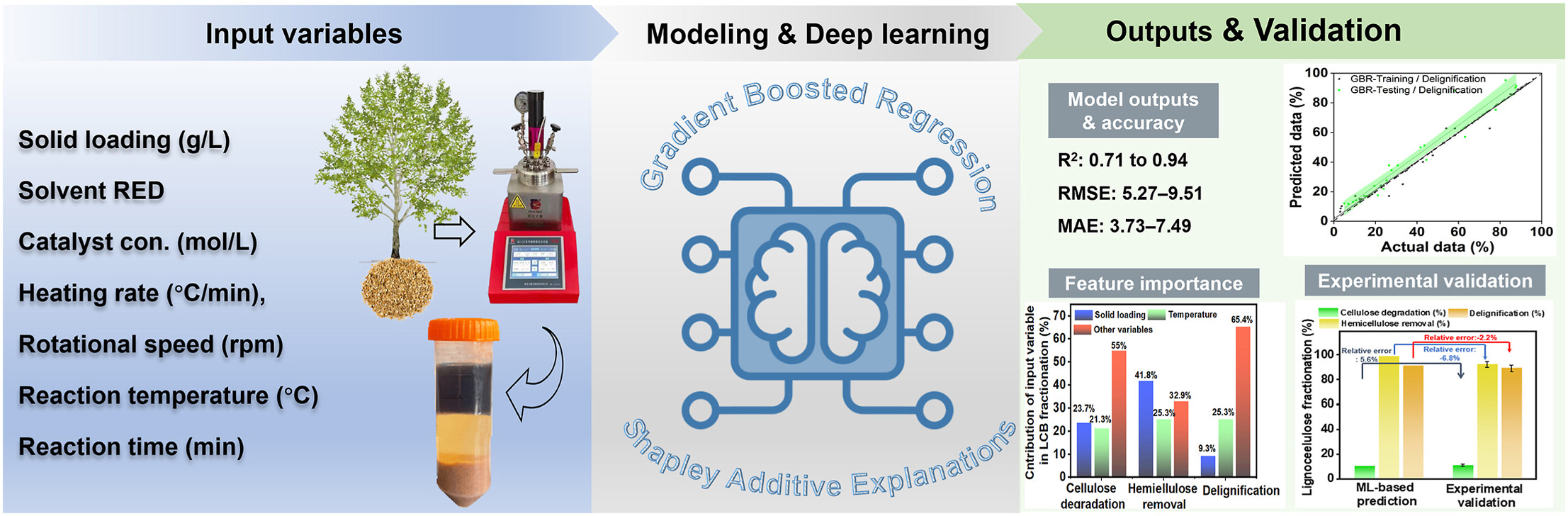
Abstract:Biphasic pretreatment efficiently fractionates lignocellulosic biomass (LCB) and holds significant potential for industrial applications. While various studies have explored parameters to improve its efficiency, the lack of an optimal framework to balance these factors restricts scalability and compromises cost-effectiveness. This study introduces a machine learning (ML) model to optimize biphasic pretreatment conditions for LCB fractionation. By leveraging ML’s capacity to uncover intricate relationships within extensive datasets, we conducted a comprehensive analysis incorporating key parameters. Feature importance analysis highlighted the critical influence of these parameters on cellulose degradation, hemicellulose removal, and delignification. The Gradient Boosted Regression (GBR) model outperformed others, achieving robust predictive metrics with R2 values from 0.71 to 0.94 and demonstrating lower error levels (RMSE: 5.27–9.51; MAE: 3.73–7.49) compared to other models during validation. Solid loading and temperature were identified as the most influential factors, contributing 23.7 % and 21.3 % to cellulose degradation, respectively. For hemicellulose removal, solid loading accounted for 41.8 %, while temperature contributed 25.3 % to delignification. The GBR-based optimization achieved 10.7 % cellulose degradation, 98.9 % hemicellulose removal, and 91.2 % delignification, with relative errors of 5.6 %, −6.8 %, and −2.2 % upon experimental validation. This ML model can revolutionize optimizing processing conditions for LCB fractionation, significantly reducing experimental time and costs while enhancing bioenergy production efficiency.
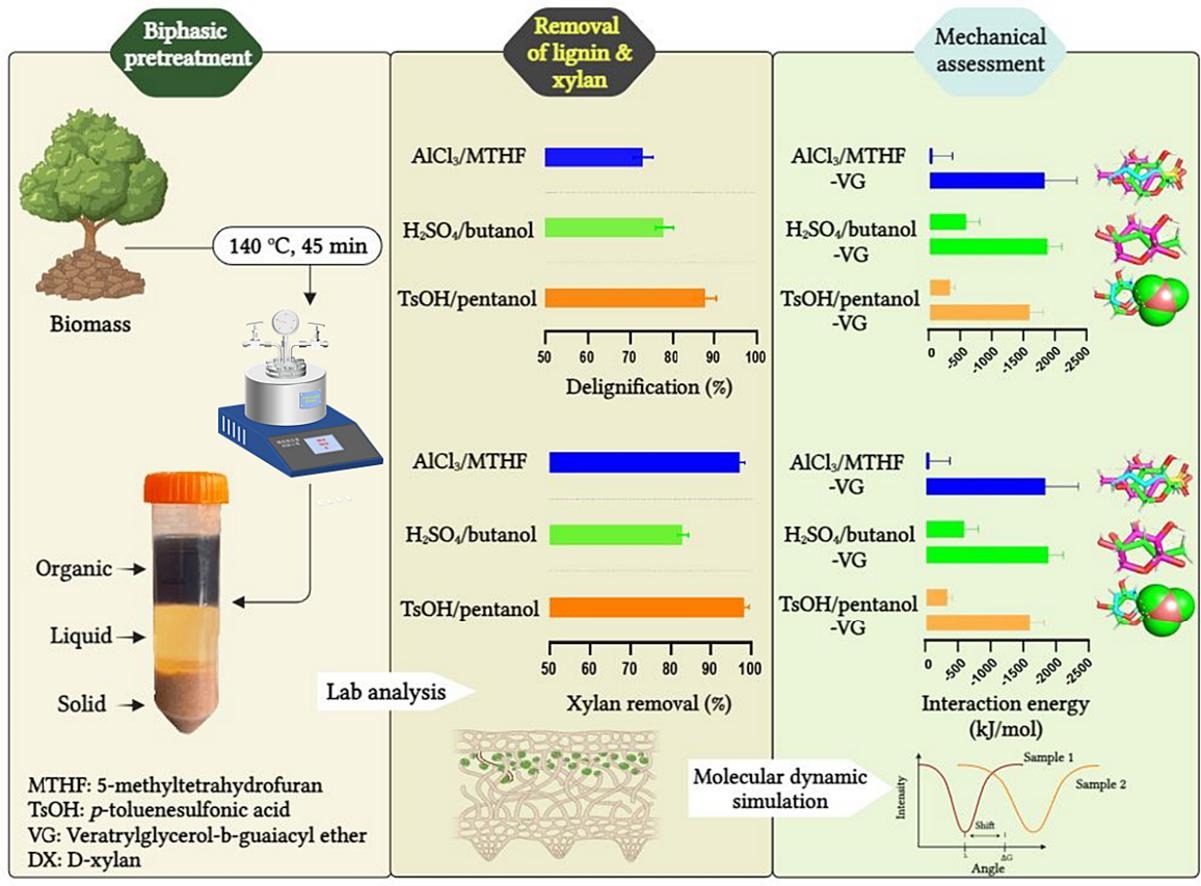
04. Transformative biorefinery model for biomass valorization into biofuel and renewable platform chemicals
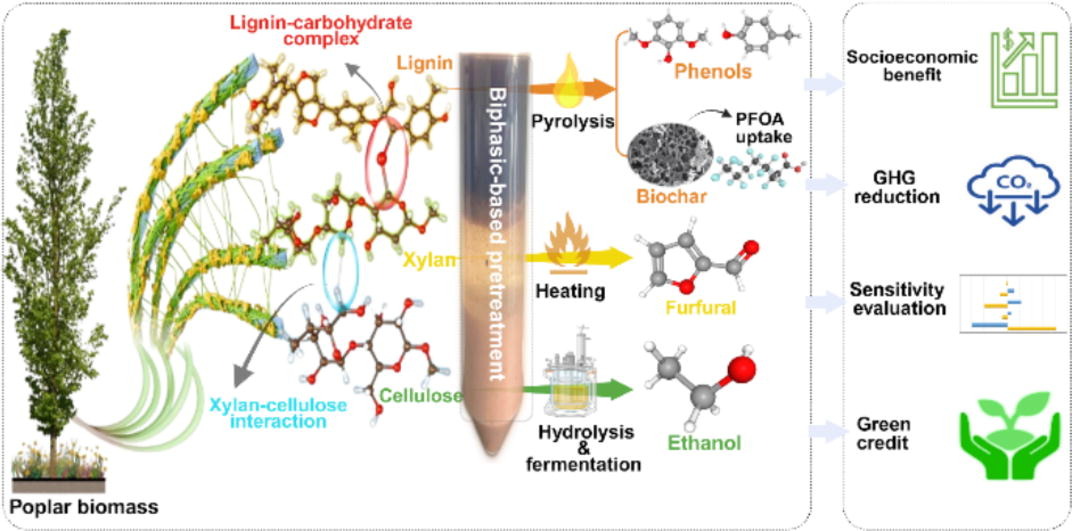
Abstract:The increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions necessitates innovative approaches to biomass utilization. This study introduces a comprehensive biorefinery model that valorizes poplar biomass into high-value products, including ethanol, furfural, phenol, and biochar. These products not only serve as promising sources for biofuel and renewable chemicals but also contribute to pollution mitigation. The approach employs a biphasic pretreatment system utilizing p-toluenesulfonic acid, pentanol, and AlCl3 under optimized conditions (120 °C for 45 min), achieving remarkable efficiencies of 95.8% xylan removal, 90.2% delignification, and 90.7% glucan recovery. The underlying mechanism, elucidated through density functional theory, demonstrates how the disruption of lignin-carbohydrate complexes via electrostatic and hydrogen-bonding interactions enhances product yields. The cellulose-rich substrate yielded 71.3 g/L ethanol, while solubilized xylan converted to 86.7% furfural without additional acid. Furthermore, lignin pyrolysis produced bio-oil containing over 45.2% phenolic compounds, while biochar demonstrated significant adsorptive capacity for perfluorooctanoic acid. Scaling this biorefinery model to process 140 million tons of poplar biomass annually reduces CO2 emissions by 75.3 million tons and provides socioeconomic savings of $17.3 billion, supporting sustainable industrial transformation.
05. Quantum Mechanical Insights into Lignocellulosic Biomass Fractionation through an NaOH-Catalyzed Triton-X 100 System: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches
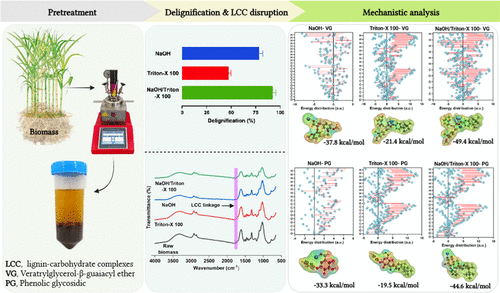
Abstract:Despite the notable efficacy of the NaOH-catalyzed Triton-X 100 system in fractionating lignocellulosic biomass (LCB), a significant gap remains in understanding the mechanistic pathways that drive this process. This study uses a dual-faceted approach, combining laboratory experiments with computational simulations to elucidate the mechanisms of delignification and lignin-carbohydrate complex (LCC) disruption. Under optimized conditions, both cellulose and hemicellulose recoveries reached around 88.5%, with delignification attaining an impressive 92.3%. Substantial changes in the physicochemical properties of the pretreated substrates were observed, including the removal of lignin and LCC-associated linkages, an enhanced crystallinity index (1.2–1.9 times), and an increase in surface area (1.2–1.4 times) compared to controls.This pretreatment system also facilitated frequent lignin depolymerization, leading to pronounced dissolution of syringyl and ferulate units. Furthermore, mechanical analyses demonstrated that this system promoted the highest interaction energy formations during LCB fractionation compared to individual NaOH or Triton-X 100 treatments alone.
06. The State-of-the-Art on Exploring Polysaccharide-Protein Interactions and Its Mechanisms, Stability, and Their Role in Food Systems
Abstract:The compatibility and assembly of dietary soft matter components are crucial in enhancing food products’ stability, nutrition, texture, flavor, and shelf life. This review emphasizes the importance of these interactions, particularly in natural polymers like polysaccharides and proteins, due to their biodegradability, versatility, and sensory contributions. The structural behavior of these polymers exhibits consolable interactions or phase separation depending on molecular arrangements, which is pivotal in determining the microstructure of food matrices. The delicate balance between attractive and repulsive forces facilitates effective self-assembly processes, while weak interactions enable essential structural adaptations. Conversely, excessive intermolecular forces or restricted molecular dynamics can result in functional instability, such as phase separation or structural collapse. This review provides an indepth examination of physical and chemical methodologies to investigate the compatibility and interactions of dietary soft matter components. Techniques such as phase modeling, turbidity analysis, microscopy, thermal analysis, rheology, and spectroscopy are employed to evaluate these materials’ suitability and assembly characteristics. By analyzing these methodologies, the review emphasizes the importance of understanding soft matter interactions for developing functional food products with improved performance and stability. Furthermore, it identifies the current challenges and limitations, offering insights into future directions for advancing food science and technology.
07. Harnessing the potential of biphasic solvent systems in lignocellulosic biomass fractionation through computational insights
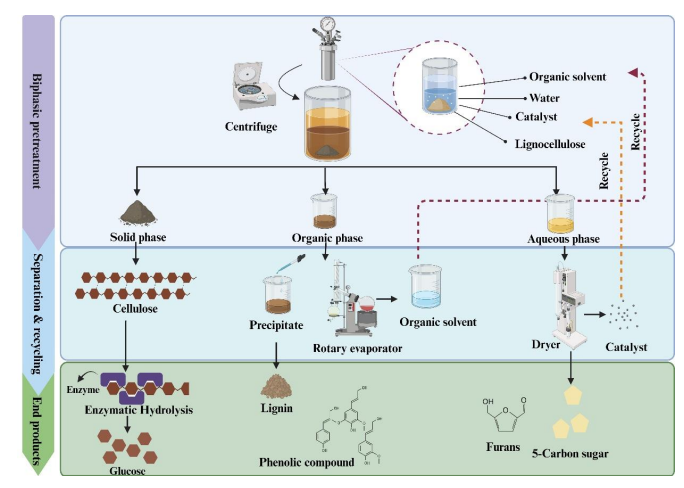
Abstract:Biphasic solvent systems have emerged as a transformative approach for the efficient fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass (LCB), driving substantial progress in biofuel and biochemical production. By precisely partitioning lignin into the organic phase and hemicellulose into the aqueous phase while maintaining cellulose within the solid fraction, biphasic systems present a sophisticated and integrative strategy for LCB processing. This dual-phase approach achieves superior product separation and significantly enhances economic viability through the recyclability of solvents and catalysts. Several biphasic systems, including those employing 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, immiscible alcohol-based systems (butanol, pentanol, and phenoxyethanol), and ketones (Methyl isobutyl ketone), have been developed for LCB fractionation. Among these, immiscible alcohol-based systems have emerged as the most effective, demonstrating the ability to minimize cellulose degradation (1.0–30.0%) while optimizing the removal of hemicellulose (80.0–98.0%) and lignin (65.0–92.0%).
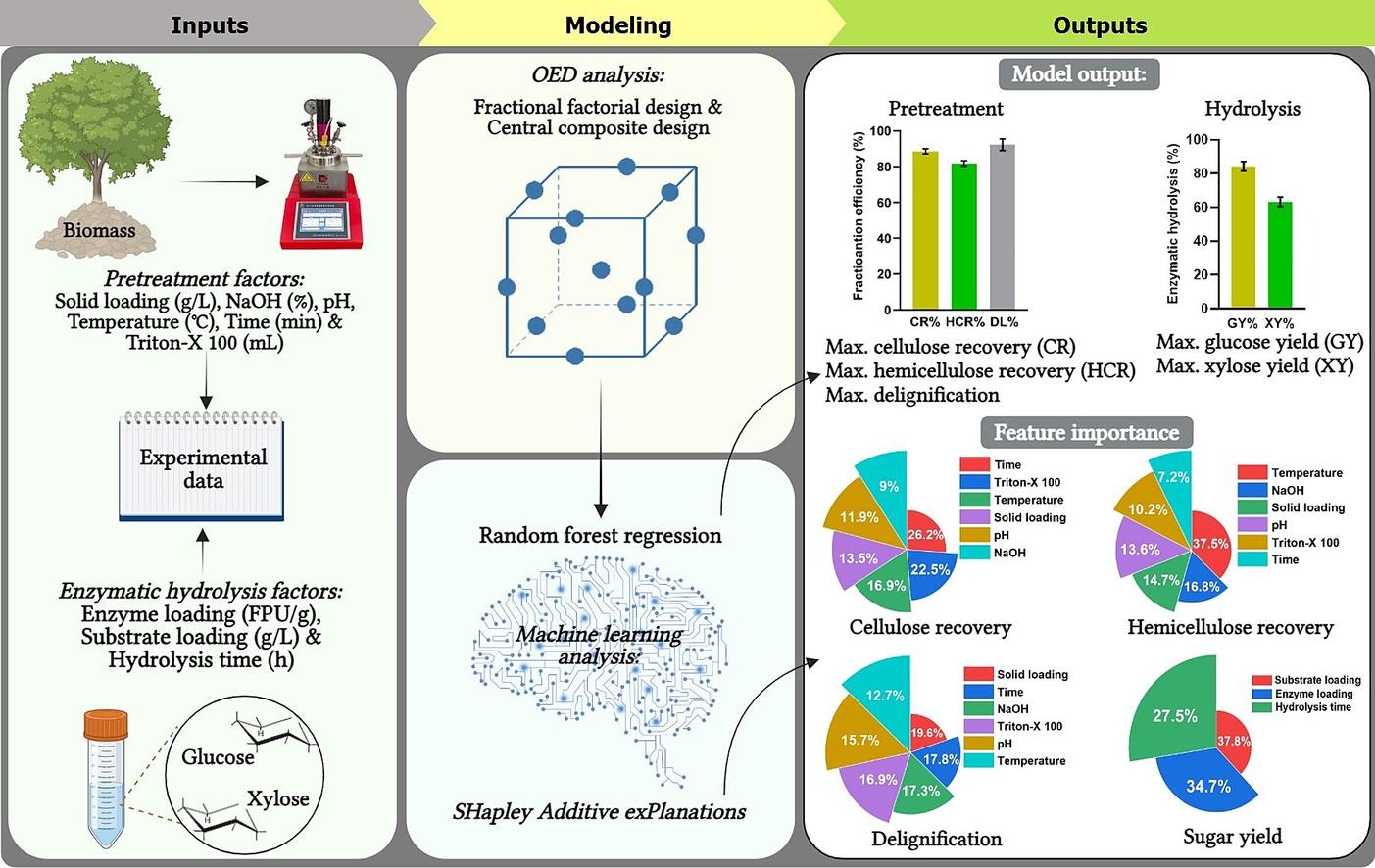
08. Machine learning-driven optimization of pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse: Analytical insights for industrial scale-up
09. Role of in situ surfactant modification of lignin structure and surface properties during glycerol pretreatment in modulating cellulase-lignin binding affinities
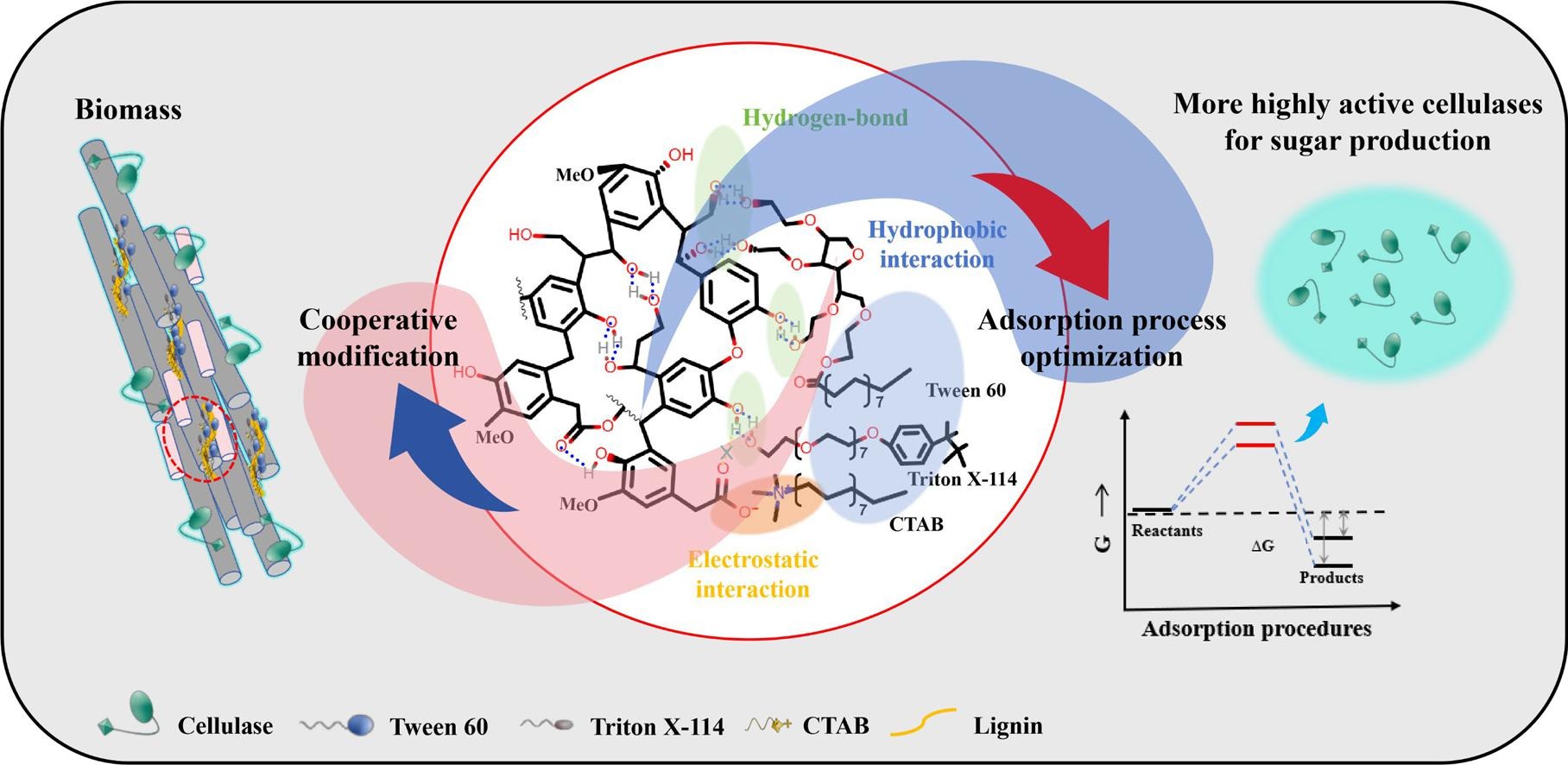
10. In-depth recognition of mixed surfactants maintaining the enzymatic activity of cellulases through stabilization of their spatial structures
11. Unveiling the mechanisms of mixed surfactant synergy in passivating lignin-cellulase interactions during lignocellulosic saccharification
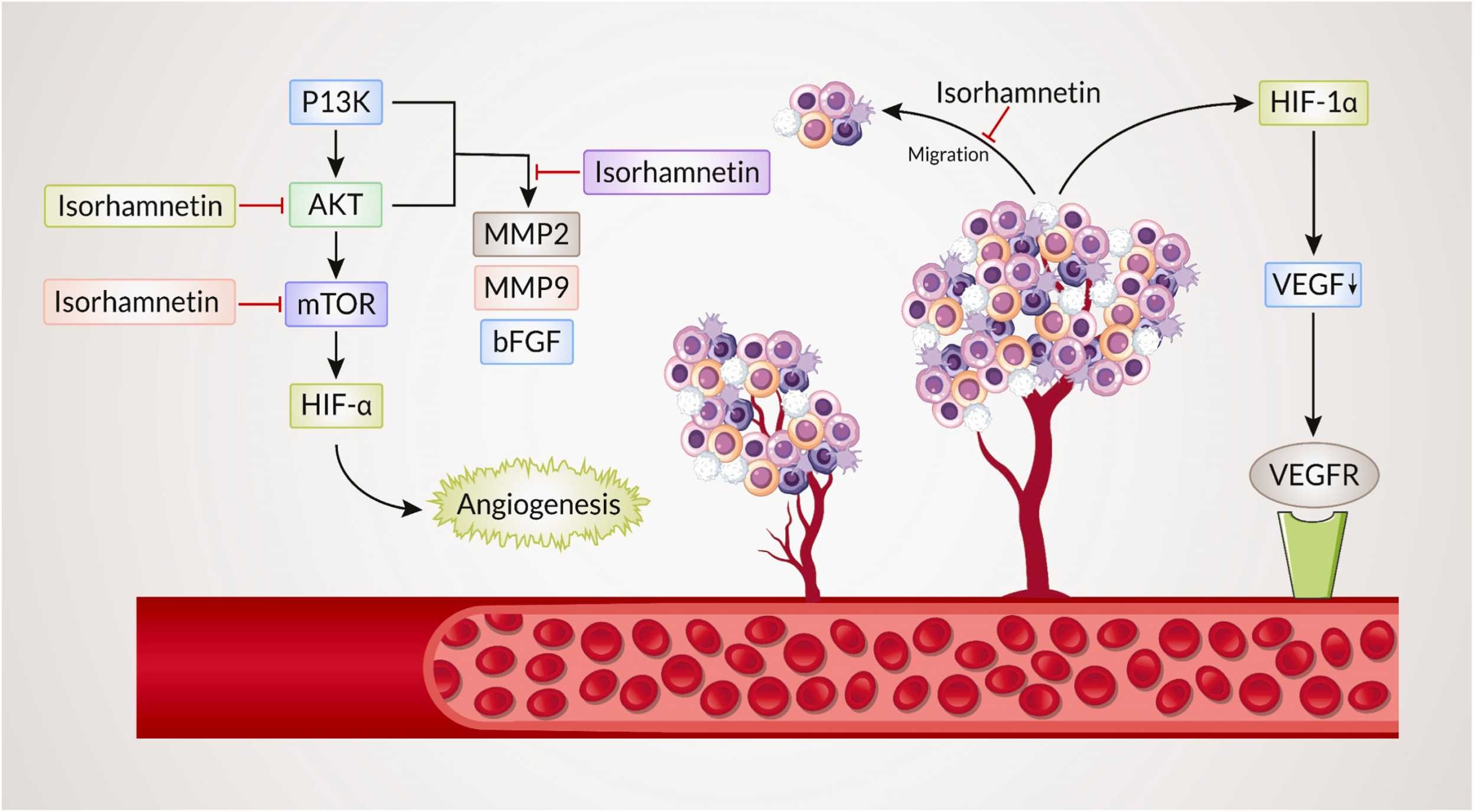
12. The experimental significance of isorhamnetin as an effective therapeutic option for cancer: A comprehensive analysis
13. Unraveling the mechanisms underlying lignin and xylan dissolution in recyclable biphasic catalytic systems
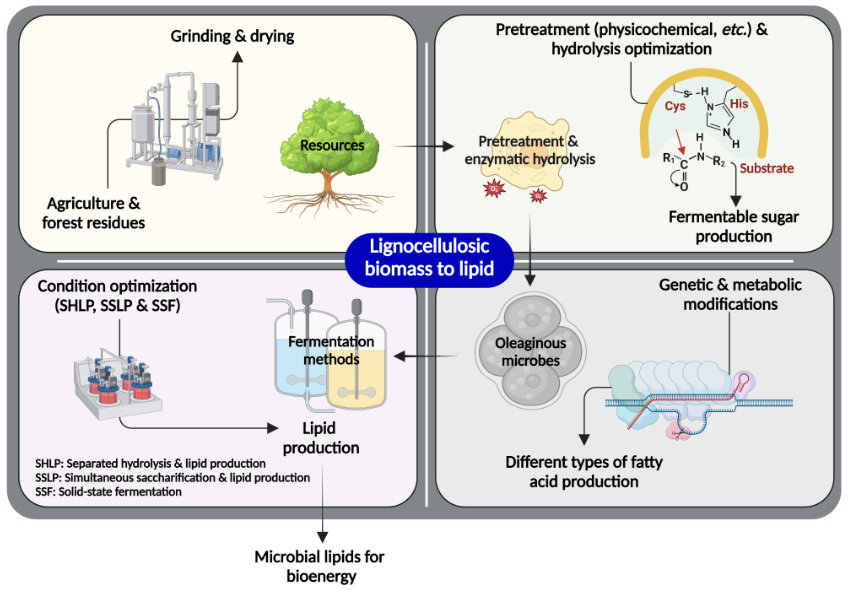
14. New trends in microbial lipid-based biorefinery for fermentative bioenergy production from lignocellulosic biomass
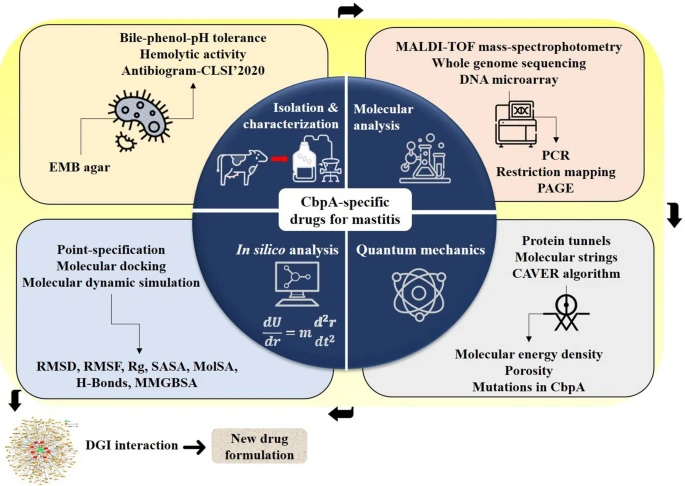
15. WGS-based screening of the co-chaperone protein DjlA-induced curved DNA binding protein A (CbpA) from a new multidrug-resistant zoonotic mastitis-causing Klebsiella pneumoniae strain: a novel molecular target of selective flavonoids
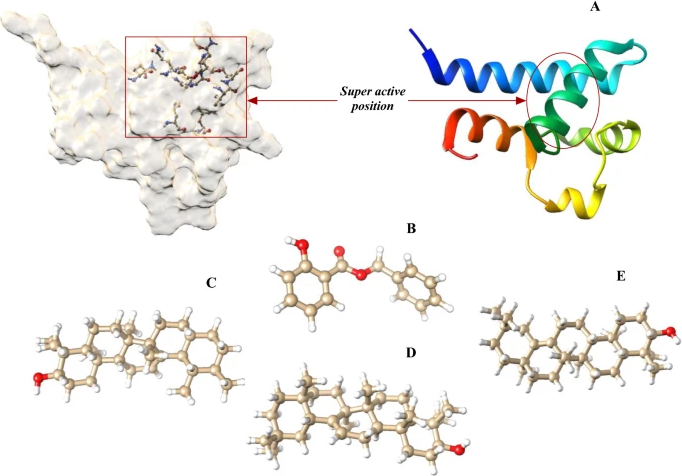
16. Target-specificity of different amyrin subunits in impeding HCV influx mechanism inside the human cells considering the quantum tunnel profiles and molecular strings of the CD81 receptor: a combined in silico and in vivo study
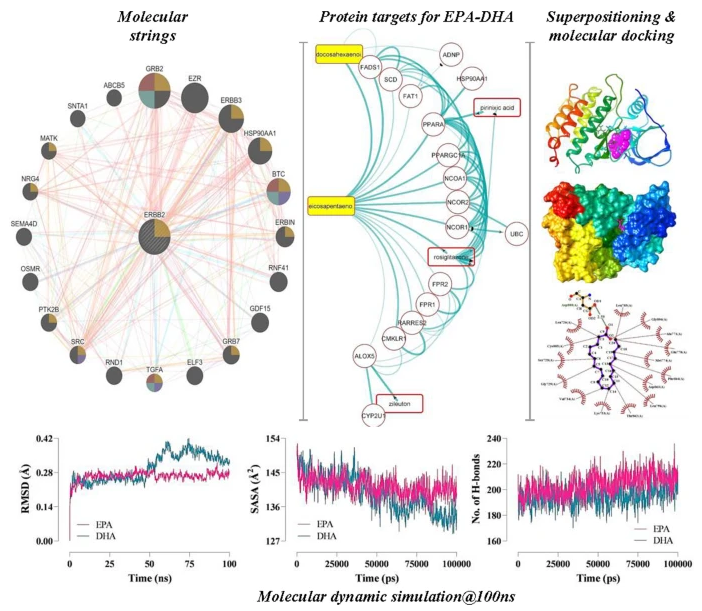
17. Oncoinformatic screening of the gene clusters involved in the HER2-positive breast cancer formation along with the in silico pharmacodynamic profiling of selective long-chain omega-3 fatty acids as the metastatic antagonists
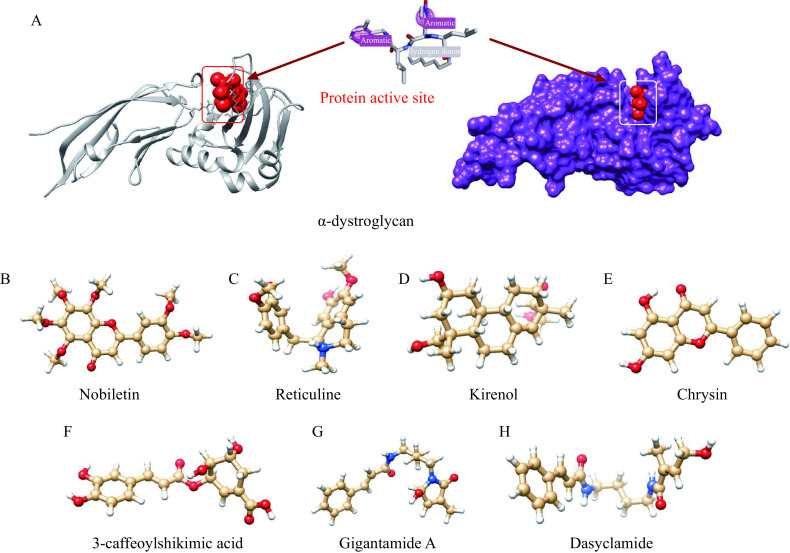
18. Target specificity of selective bioactive compounds in blocking a-dystroglycan receptor to suppress Lassa virus infection: an in silico approach
ABSTRACT
19. In ovo inoculation of duck embryos with different strains of Bacillus cereus to analyse their synergistic post-hatch anti-allergic potentialities
ABSTRACT
Background: Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, facultative anaerobic bacteria with few strains reported to be used as probiotics for animals and birds in recent times if the doses are formulated properly.
Objectives: To analyse the synergistic anti-allergic potentiality of different Bacillus cereus strains on experimental in ovo and in vitro duck model, as probiotic immune stimulant.
Materials and methods: Different strains of Bacillus cereus from 29 isolates were identifiedthrough 16S rRNA gene sequencing from the milk samples of buffalo breeds of South Asia. The probiotic properties were tested in aspects of gram staining, catalase test, coagulase, test, bile salt tolerance, pH tolerance and phenol tolerance test.
20. Molecular identification of a Bacillus cereus strain from Murrah buffalo milk showed in vitro bioremediation properties on selective heavy metals
ABSTRACT 
This study aims for molecular identification of naturally growing Bacillus cereus strain from a unique source, able to survive, and alleviate heavy metals from the nature.
Materials and Methods:
21. Molecular optimization, docking, and dynamic simulation profiling of selective aromatic phytochemical ligands in blocking the SARS-CoV-2 S protein attachment to ACE2 receptor: an in silico approach of targeted drug designing
22. A Comprehensive Analysis and Anti-Cancer Activities of Quercetin in ROS-Mediated Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells
23. ANTIVIRAL EFFECTS OF BACTERIOCIN AGAINST ANIMAL-TO-HUMAN TRANSMITTABLE MUTATED SARS-COV-2: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
24. Employment-related musculoskeletal complications experienced by the physical therapists in Bangladesh: a comprehensive cross-sectional case study
25. Catabolic profiling of selective enzymes in the saccharification of non-food lignocellulose parts of biomass into functional edible sugars and bioenergy: An in silico bioprospecting
26. Point-specific interactions of isovitexin with the neighboring amino acid residues of the hACE2 receptor as a targeted therapeutic agent in suppressing the SARS-CoV-2 influx mechanism
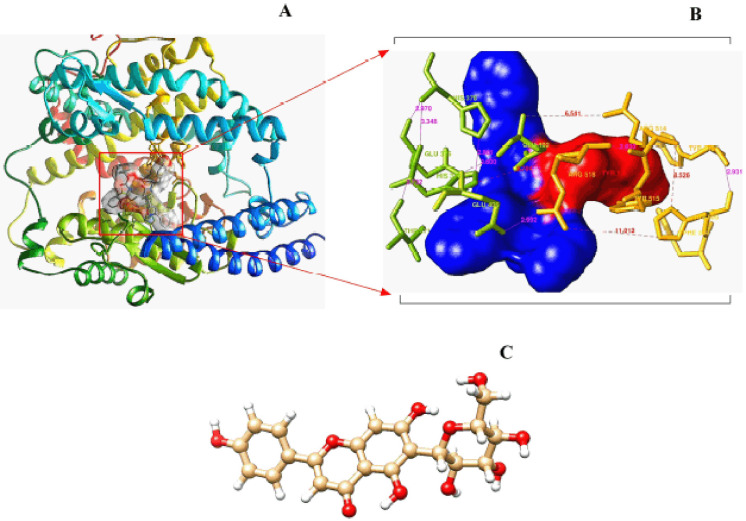
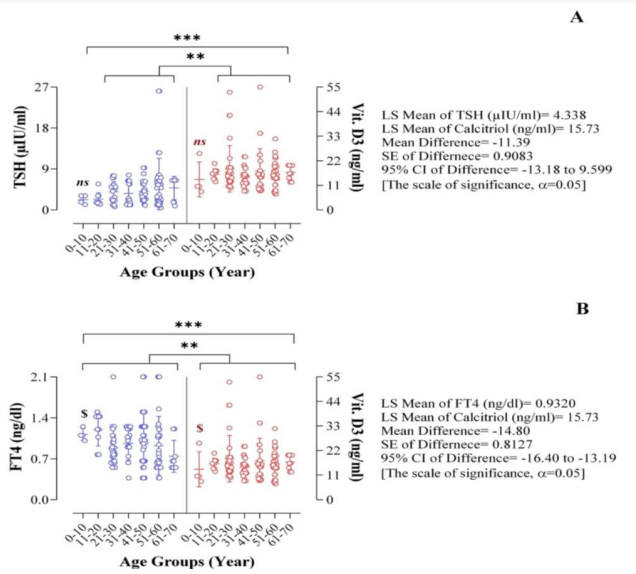
27. Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing IDA and TSH downregulation in correlation to the fluctuation of activated vitamin D3 in women
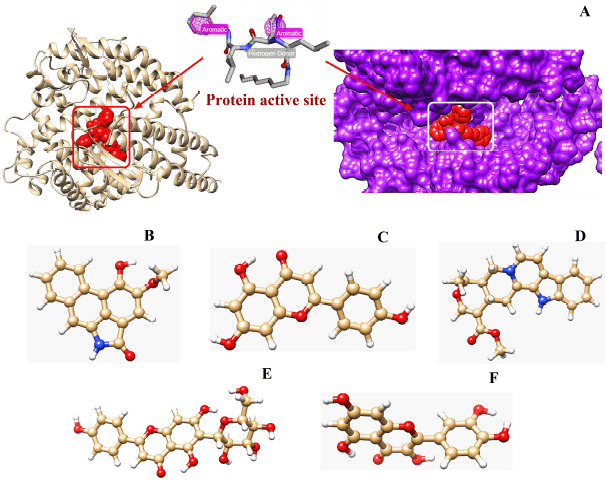
28. Active site-specific quantum tunneling of hACE2 receptor to assess its complexing poses with selective bioactive compounds in co-suppressing SARS-CoV-2 influx and subsequent cardiac injury
29. An experimental analysis of different point specific musculoskeletal pain among selected adolescent-club cricketers in Dhaka City
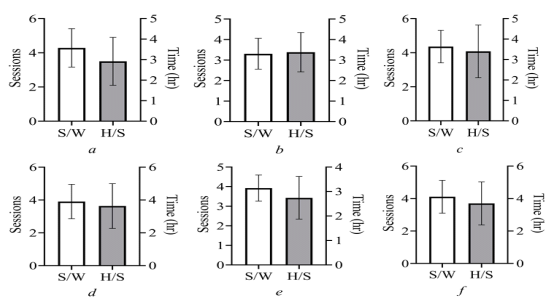
30. The Pros and Cons of Selective Renewable Energy Technologies for Generating Electricity in the Perspective of Bangladesh: A Survey-Based Profiling of Issues
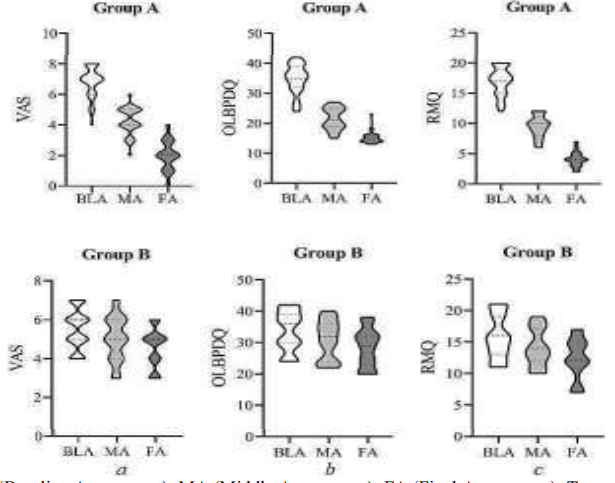
31. Original Article Effect of physical exercise and routine intervals on LBP assessment using VAS, OLBPDQ, and RMQ among professional motorbike riders in Dhaka city
32. Molecular identification, characterization, and antagonistic activity profiling of Bacillus cereus LOCK 1002 along with the in-silico analysis of its presumptive bacteriocins
Objectives: This research aimed to isolate, identify, and characterize a new strain of Bacillus cereus through different molecular biology approaches so that it could be further studied for therapeutic purposes against selective enteric pathogens.
Materials and Methods: Pure isolates of B. cereus were prepared from buffalo yogurt samples in REMBA medium. Initially, the morphological, physiological, and biochemical properties were studied accordingly. Following the tests, the molecular identification for the strain identification was conducted through plasmid DNA extraction, PCR, agarose gel electrophoresis, and 16S rRNA sequencing up to 1.37 kb. Afterward, the antibiotic sensitivity [Epsilometer test (E-Test)] and anti fungal activity were tested considering different concentrations. Being classified from the aforementioned tests, a comprehensive antimicrobial activity test was conducted using the cell-free-su pernatant (CFS) of the test strain against selective enteric pathogens in humans in vitro